A world without neurodegenerative diseases.
Disproportionate inrease in nuclear factor-kappa B p65 precipitates neuroinflammation that promotes neurodegeneration
Provaidya GILZ Analogs Inhibit Activated NF-kB
Neurodegeneration is characterized by progressive loss of structure or function of neurons that lead to varying degrees of dementia or memory loss. Alzheimer's disease accounts for two-thirds of all dementia affecting over 40 million people worldwide. There is an urgent need for vibrant drug discovery initiatives to produce efficacious therapeutic leads.
Nuclear factor-kappa B in neurodegenerative diseases
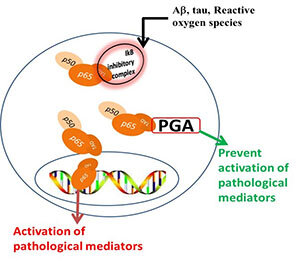
Neuroinflammation plays critical roles in the initiation and progression of neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease. The NF-κB signaling system is a dynamic protein interaction network that function as master regulators of inflammatory responses. It includes five members (p50, p52, p65 (Rel-A), c-Rel, and Rel-B), that diversely combine to form homo or hetero-dimers. In the central nervous system, activated NF-κB contributes to both neuronal survival and death. While activation of c-rel dimers elicits neuroprotective responses, that of p65 dimers primarily increases the transcription of inflammatory mediators and of endogenous beta secretase-1 (BACE-1), both of which enhance Aβ production.
Disease Modifying Threapy —— Provaidya Strategy
The goal of biological therapies is to restore the healthy balance by targeting specific molecules that promote imbalanced responses. Harnessing information from NF-kB interactome, scientists at Provaidya LLC have identified an innovative strategy to selectively target activated p65. Provaidya compounds are NF-kB interactants that bind the transactivation domain of p65 and sequester it in the cytoplasm. This prevents the nuclear translocation of activated NF-kB with consequent inhibition of transactivation of inflammatory cytokines and othat pathological mediators.